Modern trends in CNC machining

Modern trends in CNC machining
New technologies are providing new opportunities – and changing the way manufacturers handle conventional operations.
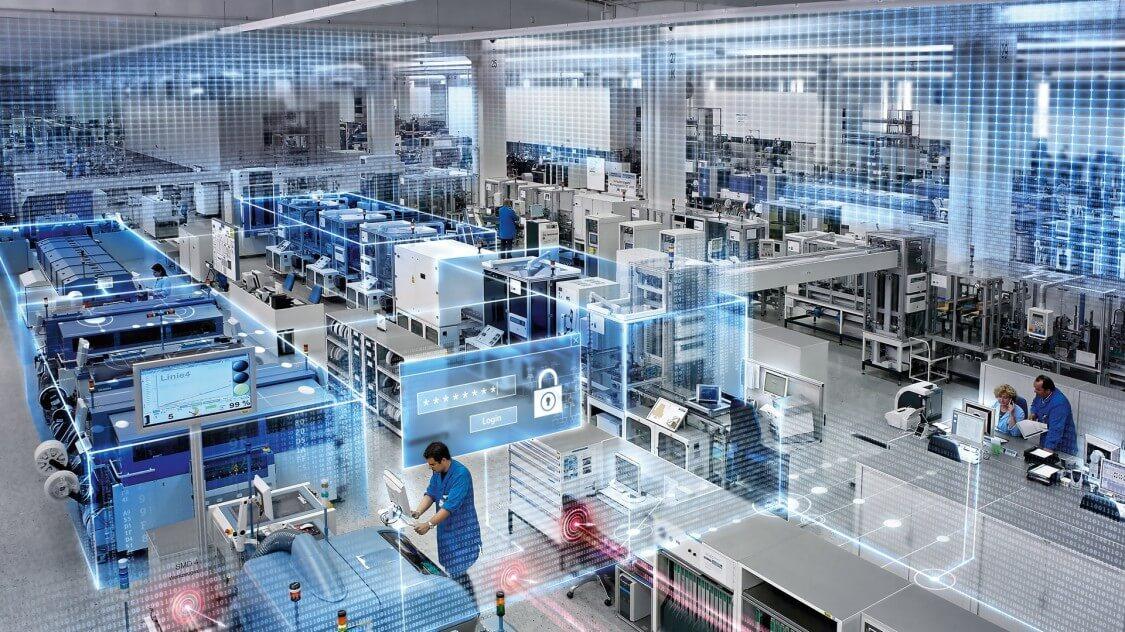
Modern technology is developing at such a rapid pace that it is shaking up the commercial world. New technologies, spanning from machine learning and artificial intelligence to the Internet of Things and cloud computing, are presenting fresh opportunities and transforming the way manufacturers approach traditional operations.
This is also what is happening in the world of precision machining. It used to be all about traditional precision metal machining, but almost everything has changed since then. Many new machining processes promise to introduce a variety of benefits, including better productivity, lower operating costs, greener and more environmentally friendly solutions and, of course, more precise tasks.
To truly understand where the world of precision parts manufacturing is headed, it’s worth considering some of the new trends. Here are some of the impending changes that are likely to have a significant impact on the current state of CNC machining.
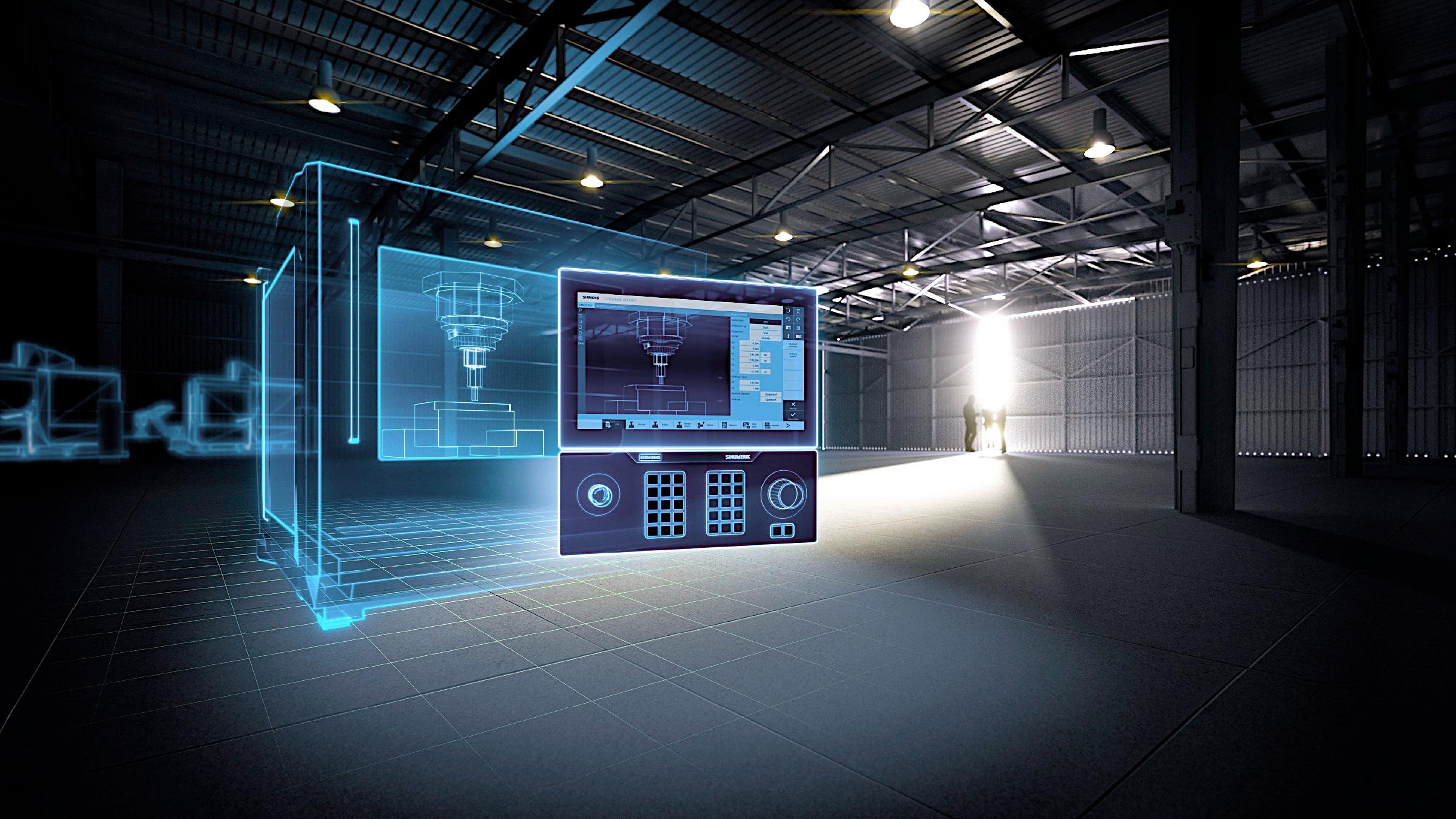
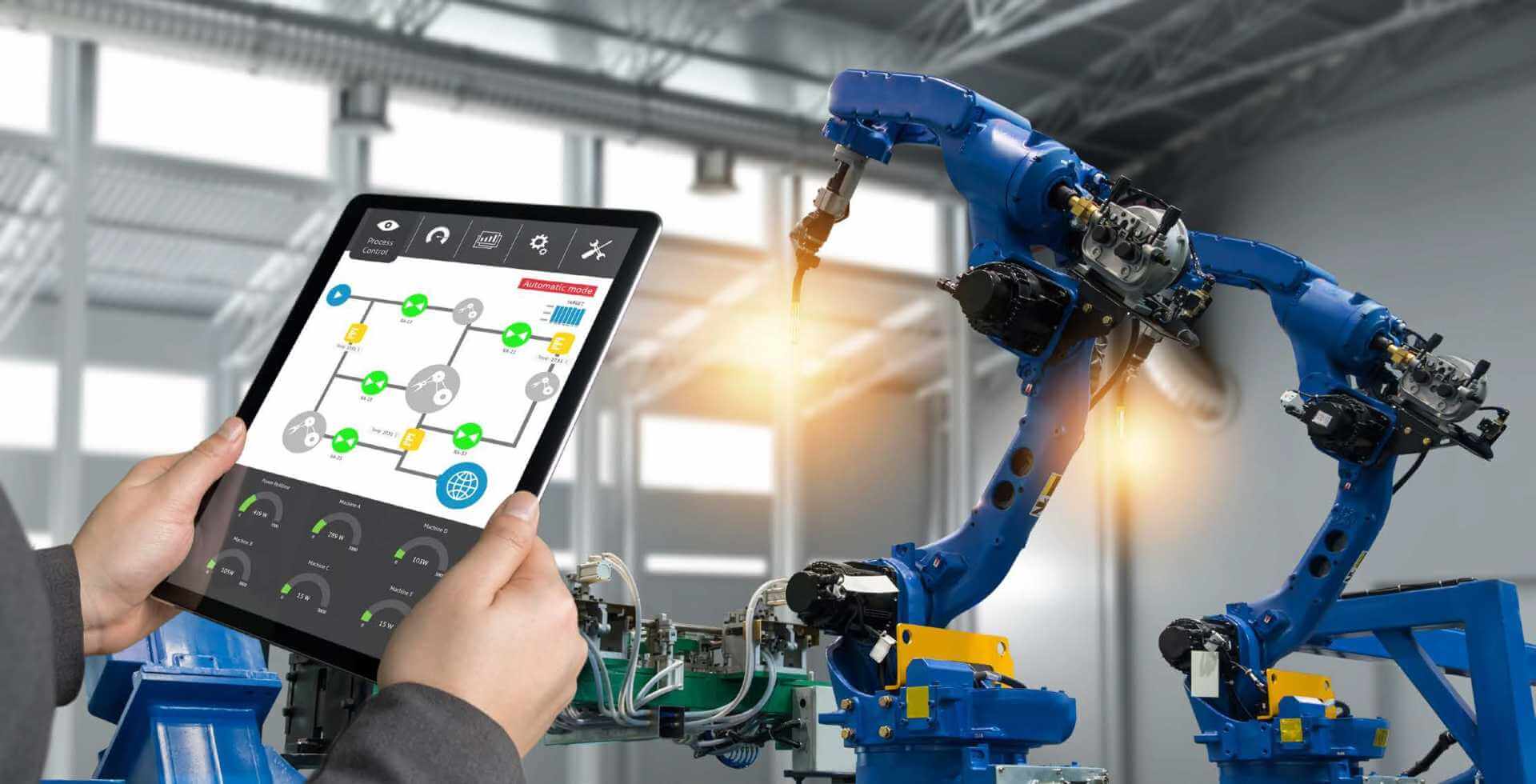
Internet of Things
A smarter, remote-controlled solution, the Internet of Things, includes smart, connected devices (including smart sensors) to improve control of various equipment and provide more information. It also complements automation systems so that processes can be fully streamlined and managed in new ways.
Various machines can then operate autonomously, requiring only human intervention or supervision when something goes wrong. But the beauty of the Internet of Things and similar technologies is that these systems can send the necessary warnings and data long before an adverse event occurs. This pre-knowledge is due in large part to the stream of real-time data that is constantly coming in and being analyzed on the fly.
Project managers and maintenance crews can keep up with equipment at a more precise time. This means they can remedy problems before they go offline or cause defects in the goods and materials being processed.
If and when a performance issue arises, the reliable information available through the Internet of Things can lead to faster resolution. Ultimately, it provides a much smoother and more efficient operation.
Laser beam machining
Laser beam machining – this innovative and relatively new method is a thermal process for removing chips or material, also known as LBM. A concentrated, high-energy laser beam is directed toward the workpiece or component, transferring thermal energy to the surface of the target. Through melting and vaporization, metallic or non-metallic target materials are removed.
Engineers can also implement welding, cladding, etching, surface machining, drilling, and cutting. It is often used to cut glass without melting or altering surrounding edges and surfaces.
Laser beam machining is becoming more widely used in manufacturing, especially for carbon fiber materials and more durable composites. It deserves its place on the list because lasers are as futuristic as can be. When you start discussing the practical application of lasers – as in LBM – it’s clear that you have an advantage.
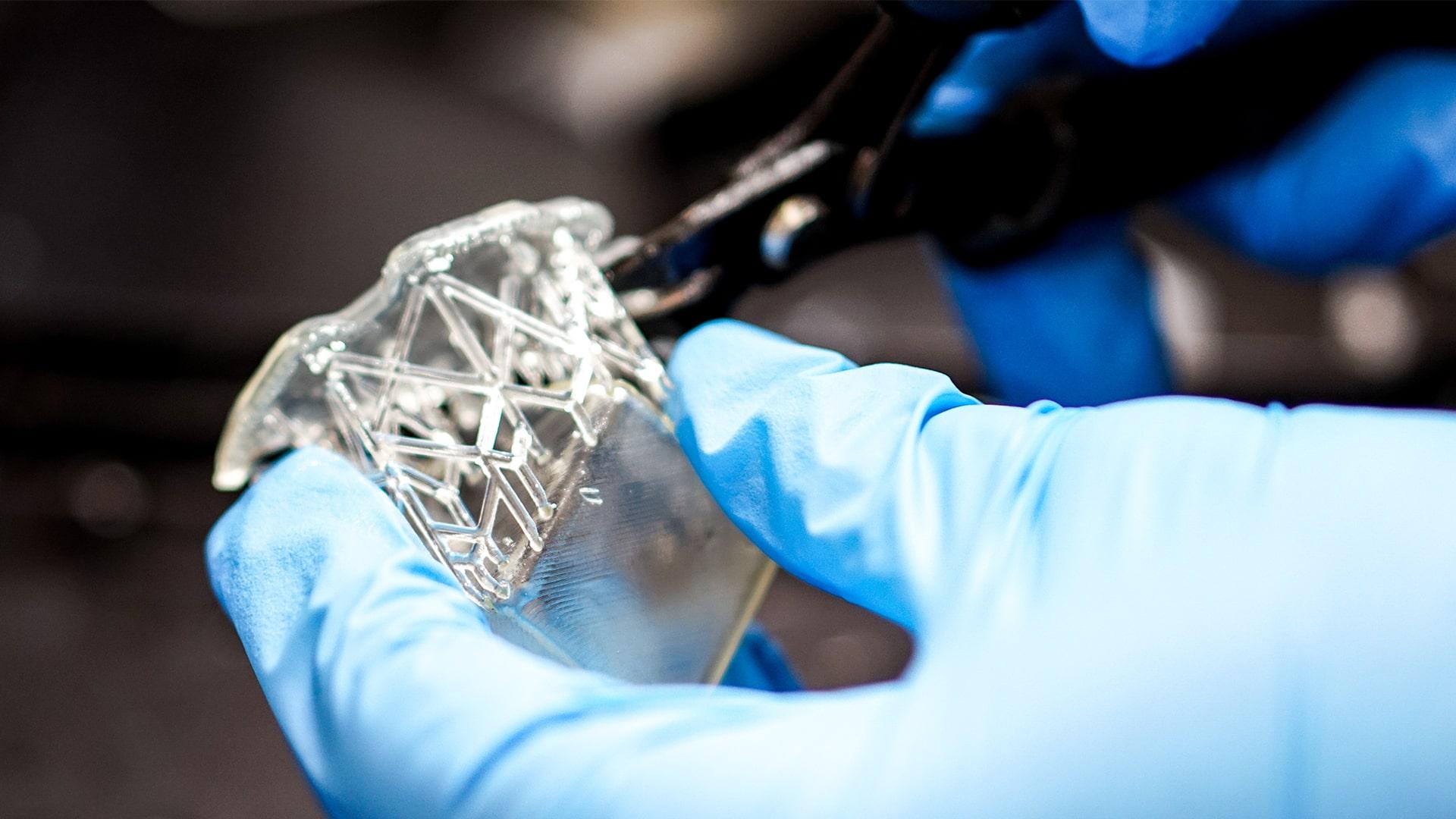
Incremental manufacturing or 3D printing
Incremental manufacturing or 3D printing – AM and 3DP have exploded in the industrial world. The first printers were designed to work only with plastics and materials like ABS, but the technology has come a long way since then. Today, they can create products and components from a variety of raw materials, including concrete, wood, steel, and a growing number of metals, alloys, ceramics, and composite materials with a metal matrix.
Hybrid machining is the most exciting trend associated with this technology: it includes both traditional CNC machining and 3D printing solutions to streamline product development. Manufacturers have much more control over the goods they create and can make changes on the fly, which means more flexibility. The entire process is faster, more efficient, and highly accurate compared to traditional machining methods. In addition, additive manufacturing changes the target or source location where manufacturing occurs.
Materials and components can be printed directly at the job site using a portable (but equally powerful) printer. The same is valid for consumer products, allowing manufacturers to create goods closer to the customer than ever before. In addition, it allows manufacturers to introduce an unprecedented degree of personalization.
Custom machining methods
Custom machining methods – Laser beam machining is not the only recent machining innovation. Other creation methods include:
Each of these is implemented differently and offers specific, effective advantages of conventional machining. For example, water jet cutting is a more subtractive process designed to trim or reduce large materials and parts. On the other hand, electrochemical machining and roller polishing are also subtractive but involve much smaller materials and adjustments.
Automated finishing systems
Automated Finishing Systems – After metal machining, resizing, or modifying metals and woods, it may be necessary to finish their outer layer or surface to achieve a shinier, more polished appearance.
While some advances have been made in this space, the processes are still relatively the same as ever. Even many new methods still use a consistent, highly repeatable process. That’s where automation comes in handy, thanks in part to today’s technologies.
Robot-operated finishing systems can change the entire process, revolutionizing the quality and productivity of the entire industry. For example, robotic blasting systems offer unparalleled improvements in output quality, productivity, versatility, and overall safety. These solutions indicate the direction in which the industry is heading toward a more efficient and automated environment.
Preparing for the future
Preparing for the future – Manufacturers can implement these technologies and trends after some time, but it is clearly necessary to understand the future their industry is heading toward. Smart, connected, and highly automated systems are a definite choice for many processes, especially highly repetitive ones. Delegating simple and repetitive tasks to human workers doesn’t make sense, especially when advanced technology can run the work faster and more efficiently.
Of course, these solutions only partially replace human workers. Instead, hardware and robotics will work with human counterparts to jointly improve the industry.