The Role of Technical Drawings in Modern Engineering
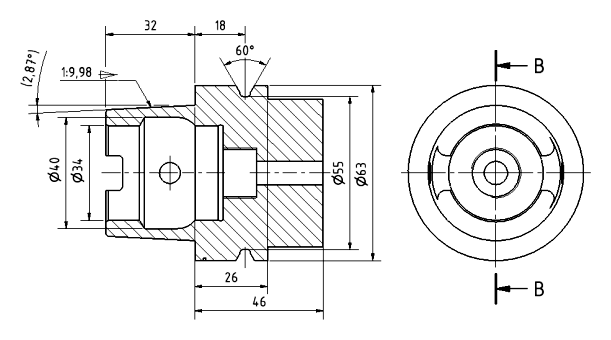
Table of contents
Technical drawings play a key role in modern engineering as an essential communication tool in design, construction, and manufacturing. Their history dates back to the 18th century when Gaspard Monge developed the principles of drafting geometry, which has become the foundation of modern drawing methods.
Modern technical drawings, both two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D), can accurately represent design concepts. The development of computer technology, such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, has revolutionized how drawings are created and analyzed, making them more accurate and efficient.
This article introduces the importance of technical drawings, describes the modern tools used in their creation, and discusses their use in various industries. Issues concerning the future of technical drawings in the context of the dynamic development of technology will also be addressed.
Importance of Technical Drawings
Technical drawings are the universal language of communication in engineering and technology. They are an indispensable part of the design process, enabling precise communication of information regarding dimensions, shapes, materials, and assembly methods. Their role includes:
Technical drawings promote efficiency and precision and enable modifications and improvements at the planning stage, making them a key tool in modern engineering. Their flexibility allows designs to adapt to changing technological and market requirements.
With advanced CAD tools, engineers can test alternatives and run simulations, minimizing the risk of errors and improving decision-making. In addition, technical drawings support innovation processes, enabling the easy implementation of new concepts and adaptation to dynamically changing production and operating conditions.
Modern Tools and Technologies
The development of computer technology has revolutionized how technical drawings are created. Modern tools, such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, allow design in two and three dimensions (2D and 3D), significantly increasing engineers’ work’s precision and efficiency.
CAD makes modifying designs, automatically generating documentation, and performing simulations easy. Programs such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, CATIA, and Fusion 360 support modeling, testing, and analysis processes, eliminating the need for costly physical prototypes. With CAD tools, engineers can create precise engineering drawings that are easy to update and integrate with other engineering systems. CAD also enables the automatic generation of bill of materials (BOM) and technical documentation, speeding up the process of preparing designs for production.
Advanced CAD features include parametric modeling tools that allow easy changes to a design while maintaining the integrity of all related elements. The programs also allow users to create motion animations and simulate the operation of mechanisms, allowing them to detect potential problems before production begins.
Integrated analysis modules enable strength and thermal analysis without exporting data to external applications. This allows the entire design and testing process to occur in a single environment, saving time and increasing efficiency.
Cloud computing and product data management (PDM) platform integration enables real-time team collaboration. Engineers can simultaneously work on a project, track changes, and ensure compliance with design requirements, regardless of location.
3D modeling has become a standard in many industries, enabling visualization of complex structures, dynamic analysis, and testing of components before production. Integration with finite element analysis (FEA) and flow simulation (CFD) tools allows accurate testing of the strength and functionality of designs.
3D printing is another breakthrough that allows rapid prototyping and testing of components without involving costly manufacturing processes. Modern 3D printers work directly with CAD programs, streamlining the process from design to physical model.

Applications in Various Industries
Construction
Technical drawings play a key role in the construction industry, providing the basis for architectural, structural, and installation designs. They allow for developing detailed plans for buildings, foundations, and installation layouts, such as electrical, water, and sewage systems. Thanks to these documents, it is possible to precisely determine the dimensions, materials, and installation techniques, which ensures compliance with building standards and construction safety.
Technical drawings accurately depict building plans, foundations, electrical, water, and sewage system layouts. With detailed specifications, technical drawings facilitate coordination between architects, construction engineers, and contractors. They also clearly define the scope of work, schedules, and technical requirements, minimizing the risk of mistakes and misunderstandings on the construction site.
Modern CAD technologies allow rapid changes and adaptation of designs to changing construction conditions, which minimizes the risk of construction errors and schedule delays. In addition, BIM (Building Information Modeling) models enable the creation of digital building twins that support clash analysis, energy simulations, and cost optimization.
Mechanical industry
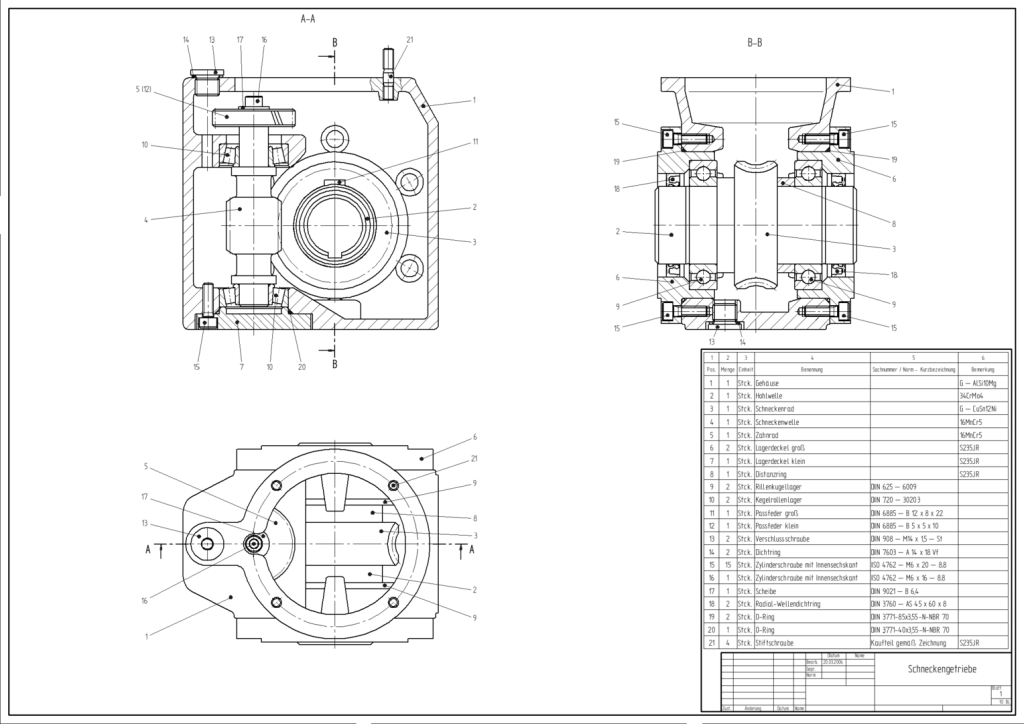
In the mechanical industry, engineering drawings are a key tool in designing machinery, equipment, and tools. They allow the precise determination of dimensions and tolerances, ensuring compliance with manufacturing requirements. Thanks to modern CAD tools, three-dimensional (3D) models can be created that facilitate dynamic analysis, load simulations, and functional tests.
Assembly drawings enable the precise assembly of parts while manufacturing drawings contain detailed technological data for machining, welding, or component assembly. Finite element analysis (FEA) allows for the prediction of structural strength.
Electronics
Engineering drawings are key in designing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electrical schematics in electronics. They enable precise representation of circuits, such as conductive paths, solder points, and component placement. With Electronic Design Automation (EDA) tools, circuits can be modeled and tested even before they are physically fabricated, minimizing the risk of errors and optimizing designs for performance.
EDA tools also allow for the simulation of electrical system operation, signal analysis, and checking of compliance with electromagnetic (EMC) standards. Software such as Altium Designer, KiCad, and Eagle generate schematic diagrams, design PCBs, and create production files for assembly machines.
With 3D rendering capabilities, engineers can visualize circuits in space, which helps detect potential assembly problems. Modern technology also allows integration with thermal and mechanical analysis tools to assess the strength and cooling of electronic components.

The Future of Technical Drawings
The future of technical drawings is centered on the continued development of digital technologies and the integration of new design tools. Building Information Modeling (BIM), augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) are becoming the standard for visualizing projects.
BIM enables the creation of intelligent 3D models that integrate data on geometry, materials, and construction schedules. AR and VR, on the other hand, allow interactive presentations of projects, making it easier to identify potential problems before construction work begins. These technologies enable virtual walk-throughs of designed facilities, which benefit investor presentations and training processes.
Automation of design processes, including generative design based on artificial intelligence, speeds up the creation of complex structures and optimizes production costs. AI algorithms analyze massive data sets and propose optimal design solutions that meet technical and economic requirements. Machine learning supports design optimization by analyzing previous patterns and suggesting improvements.
3D printing enables the rapid creation of prototypes and components, minimizing the time and cost of project implementation. This technology makes it possible to produce complex components that would be difficult to manufacture using traditional methods. Engineers can test these components early in design, eliminating errors before mass production begins.
In the future, it will become increasingly important to use artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze design data and the Internet of Things (IoT), which enables real-time monitoring of component status. Integrating AI and IoT with engineering drawings will create digital twins (digital twins) that simulate the operation of real objects, enabling ongoing monitoring and optimization of system performance.
The role of technical drawings in modern engineering – Summary
Technical drawings remain an indispensable part of modern engineering. They play a key role in the design, manufacturing, and operational processes, ensuring precision, efficiency, and communication between specialists from different disciplines. The development of digital technologies, such as CAD, BIM, AR/VR, and integration with AI and IoT, has further increased their functionality and application.
Modern tools allow for the automation of design processes, data analysis, and solution testing before implementation, minimizing errors and costs. In turn, technologies such as 3D printing open up new possibilities for prototyping and manufacturing.
The future of technical drawings seems inextricably linked to the further development of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and digital twins, enabling even more dynamic and precise project management. Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) will provide real-time monitoring and optimization of systems, which will contribute to greater operational efficiency.
In summary, engineering drawings will remain a fundamental engineering tool, adapting to the changing technologies and requirements of the modern world. Their evolution will be driven by the need for innovation, precision, and sustainability, making them an even more essential part of contemporary engineering.